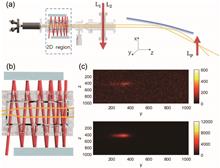
Accurate control of magnetic fields is crucial for cold-atom experiments, often necessitating custom-designed control systems due to limitations in commercially available power supplies. Here, we demonstrate precise and flexible c
Studying Rydberg microwave frequency comb (MFC) spectroscopy helps increase the working bandwidth of the Rydberg receiver. This Letter demonstrates off-resonant Rydberg MFC spectroscopy in a meta-waveguide-coupled Rydberg atomic s
Isotope shifts among different isotopes can be effectively addressed using narrow-linewidth lasers, facilitating laser isotope separation and achieving significant enrichment at a single stage. The separation of potassium isotopes
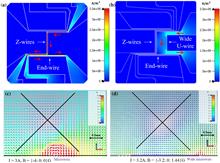
We developed a new single-layer atom chip with an additional U-shaped current-carrying structure. The new U-shaped microwire creates optimized magnetic field distribution, which increases the trapping volume of a magneto-optical t
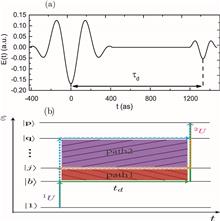
We propose a scheme that utilizes weak-field-induced quantum beats to investigate the electronic coherences of atoms driven by a strong attosecond extreme ultraviolet (XUV) pulse. The technique involves using a strong XUV pump pul
To obtain cold atom samples with temperatures lower than 100 pK in the cold atom physics rack experiment of the Chinese Space Station, we propose to use the momentum filtering method for deep cooling of atoms. This paper introduce
We experimentally demonstrate third-harmonic generation (THG) in gases ionized by a femtosecond laser pulse superimposed on its second-harmonic (SH). The mechanism of THG has been investigated, and it demonstrates that a third-ord
We report the measurement of the electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) with Rydberg states in ultracold K40 Fermi gases, which is obtained through a two-photon process with the ladder scheme. Rydberg–EIT lines are obtaine
We report two ultra-stable laser systems automatically frequency-stabilized to two high-finesse optical cavities. By employing analog-digital hybrid proportional integral derivative (PID) controllers, we keep the merits of wide se
We report the experimental realization of dark state atoms trapping in a nanofiber optical lattice. By applying the magic-wavelength trapping potentials of cesium atoms, the AC Stark shifts are strongly suppressed. The dark magnet
We present the frequency control of a 759 nm laser as a lattice laser for an ytterbium (Yb) optical clock. The frequency stability and accuracy are transferred from the Yb optical clock via an optical frequency comb. Although the
An ultranarrow bandwidth Faraday atomic filter is realized based on cold Rb87 atoms. The atomic filter operates at 780 nm on the 52S1/2, F=2 to 52P3/2, F′=3 transition with a bandwidth of 7.1(8) MHz, which is approaching the natur
In this article, taking advantage of the special magnetic shieldings and the optimal coil design of a transportable Rb atomic fountain clock, the intensity distribution in space and the fluctuations with time of the quantization m
We take H++CO as a prototype to analyze the effect of ion or proton collision on molecular orientation modulated by a two-color shaped pulse combined with the time-delayed terahertz (THz) pulse. Through examining the effect of ion
The gravimeter based on atom interferometry has potential wide applications on building gravity networks and geophysics as well as gravity assisted navigation. Here, we demonstrate experimentally a portable atomic gravimeter opera
The nitrogen vacancy (NV) center in diamond has been well applied in quantum sensing of electromagnetic field and temperature, where the sensitivity can be enhanced by the number of NV centers. Here, we used electron beam irradiat
A cavity-stabilized 578 nm laser is used to probe the clock transition of ytterbium atoms trapped in optical lattice sites. We obtain a Fourier-limited 4.2-Hz-linewidth Rabi spectrum and a Ramsey spectrum with fringe linewidth of
We demonstrate two ultra-stable laser systems at 1064 nm by independently stabilizing two 10-cm-long Fabry–Pérot cavities. The reference cavities are on a cubic spacer, which is rigidly mounted for both low sensitivity to environm
Nonsequential double ionization (NSDI) of noble gas atoms in counter-rotating two-color circularly polarized (CRTC) laser fields is investigated. A scaling law is concluded by qualitatively and quantitatively comparing the momentu
Coulomb potential may induce a significant angular offset to the two-dimensional photoelectron momentum distributions for atoms subject to strong elliptically polarized laser fields. In the attoclock experiment, this offset usuall